NREL's storage projections for 2050
- The National Renewable Energy Laboratory's (NREL) last report on the future of storage provides "key learnings" from a series of six extensive research studies.
NREL has presented eight "key learnings" in a freshly published report, often in the form of projections. Below is a condensed version.
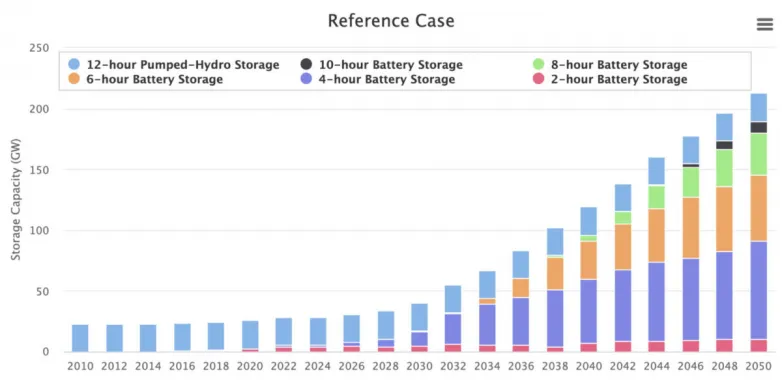
Battery releases in the USA will certainly enhance storage space capacity to 200 GW as well as 1,200 GWh in 2050 in the recommendation case, as displayed in the picture above. Pumped hydro storage capacity will certainly not enhance.
Lithium-ion batteries will continue to have the greatest market share "for a long time," as system expenses for four-hour storage space, consisting of all system components as well as installment, be up to $200/kWh capacity by 2030, and remain to decline. Other innovations "might have brand-new opportunities" if they can compete with battery costs.
The ability to offer solid capacity-- which is the greatest value of storage-- depends upon the fit in between storage period as well as the duration of the area's web top tons. Company capacity makes it possible for storage to meet need during system peak times and to replace gas wind turbines.
" Time changing," or conserving energy for discharge sometimes of high need, provides a smaller sized yet still substantial part of the value of storage. Providing operating gets includes very little value, because of "saturation" of book requirements from storage released for other reasons. The value of postponing transmission by including storage was not approximated, as it is "hard to isolate, and also extremely regionally details."
Offered the "mainly untapped possible flexibility in end-use electrical power demand," storage faces competition from grid flexibility alternatives such as time-varying retail prices as well as industrial demand action.
Storage and solar power are corresponding, as boosted release of PV shortens the peak net lots period, so that shorter-duration storage, at reduced price, can couple with PV to supply solid capacity. The lower prices to supply solid capacity translate to enhanced storage releases.
Driving a pattern in the opposite instructions, as storage implementations enhance, the web top lots become bigger, needing longer-duration storage space to provide the same degree of firm capacity. Therefore, storage periods "will likely enhance" as storage space deployments increase. As shown in the photo above, implementation of six-hour batteries would certainly start around 2034 in a recommendation case, as well as release of eight-hour batteries would start around 2040. This vibrant "presents chances" for emerging innovations efficient in longer durations, "and even for the next generation of existing modern technologies" such as pumped storage space hydropower.
Customer fostering of building-level storage will enhance as storage expenses decline and also if the value of backup power is regarded to be greater. On the whole, the customer adoption capacity will certainly be less than the financial possibility due to lengthy repayment durations. At low battery costs and also very low PV prices, dispersed storage could get to 82 GWh by 2050.
Seasonal storage space innovations end up being "especially important" for 100% clean power systems, for keeping excess generation in the springtime as well as autumn and also shifting energy supply to the summer and winter season. Greater than 400 GW of seasonal storage space capacity, such as combustion generators fueled by renewably derived hydrogen, would be required for 100% clean power.
The report concludes by listing continuing to be uncertainties that "might change the trajectories for storage growth as well as evolution." The report briefly explains each of the 6 previous NREL research studies on which it is based.
Also read

