Towards brand-new solar cells with energetic learning
- Exactly how can I prepare myself for something I do not yet know? Researchers from the Fritz Haber Institute in Berlin and also from the Technical University of Munich have addressed this almost philosophical inquiry in the context of artificial intelligence. Learning is no more than making use of prior experience. In order to handle a new circumstance, one requires to have actually taken care of roughly comparable situations prior to.
In machine learning, this correspondingly implies that a learning algorithm needs to have been exposed to roughly similar information. Yet what can we do if there is a nearly limitless amount of possibilities so that it is merely impossible to create information that covers all scenarios?
This issue shows up a great deal when taking care of an unlimited number of feasible candidate molecules. Organic semiconductors allow vital future innovations such as mobile solar cells or rollable display screens.
For such applications, enhanced organic molecules - which make up these materials - require to be found. Jobs of this nature are progressively making use of methods of machine learning, while training on information from computer system simulations or experiments.
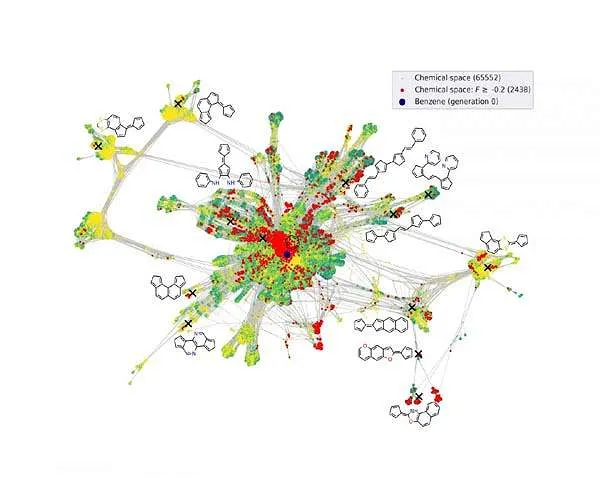
The variety of potentially feasible little natural molecules is, nonetheless, estimated to be on the order of 1033. This frustrating variety of opportunities makes it practically impossible to produce adequate information to show such a large product diversity. In addition, much of those molecules are not also ideal for natural semiconductors. One is essentially looking for the typical needle in a haystack.
In their work released lately in Nature Communications the group around Prof. Karsten Reuter, Supervisor of the Theory Department at the Fritz-Haber-Institute, addressed this issue utilizing supposed energetic learning. As opposed to learning from existing information, the maker learning algorithm iteratively determines for itself which data it in fact needs to learn about the trouble.
The researchers first execute simulations on a few smaller molecules, as well as get information connected to the molecules' electrical conductivity - an action of their efficiency when looking at feasible solar cell products. Based on this data, the formula chooses if little modifications to these molecules could already cause beneficial residential properties or whether it doubts because of a lack of comparable information.
In both cases, it immediately requests brand-new simulations, enhances itself through the recently created data, considers brand-new molecules, and also takes place to duplicate this treatment.
In their work, the scientists demonstrate how brand-new and also encouraging molecules can successfully be determined this way, while the algorithm continues its exploration into the substantial molecular room, even now, at this actual minute. Every week new molecules are being suggested that could introduce the future generation of solar cells as well as the algorithm just keeps improving and much better.
Also read

