Scientists investigate methods for thermal evaporation and hybrid deposition of perovskite solar cells and also mini-modules
- Scientists from Singapore's Nanyang Technological University have actually examined exactly how thermal evaporation (TE) could be used to produce small perovskite solar modules. TE are fully grown techniques that are typically utilized in the microelectronic and optoelectronic markets to create natural light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), metal contacts, as well as various coatings.
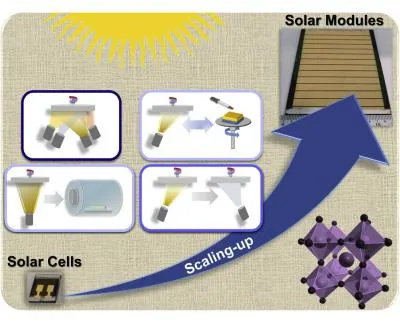
The research study team analyzed using numerous evaporation-based techniques to fabricate halide perovskite thin films, from the reasonably straightforward single-source deposition and also multi-source co-evaporation to the extra complicated multistep evaporation and also hybrids of thermal evaporation with gas response and remedy handling. The team discussed that this mixed method exploits the advantages of both methods, yet likewise has some constraints, such as boosted complexity as well as the use of solvents.
The group specified that it believes that thermal evaporation is the excellent perovskite deposition method to make that jump quickly, since it is quickly scalable, without hazardous solvents, as well as already well-integrated into existing opto- and also microelectronics production lines.
The researchers stated among the primary issues with co-evaporation is the requirement for comprehensive optimization of the deposition specifications for perovskites with intricate stoichiometries, particularly when more than two or three precursors are evaporated at the same time. They likewise kept in mind how long deposition time can provide an obstacle for commercial production, as most research studies of these techniques tend to neglect this issue.
Their review provided a collection of techniques to fabricate both perovskite solar cells and also mini modules. These methods include one-step thermal evaporation, multi-step thermal evaporation, and also multi-step hybrid deposition.
"It would be preferable to generate not just evaporated perovskite films but also fully evaporated modules making use of the same fabrication lines," the study group claimed.
The advantages reportedly consist of a high degree of process control, exactly controllable film thickness, easy sequential enhancement of several layers, as well as low-substrate temperature level processability. The researchers assert that the methods can likewise enable far better purification of the forerunners during film formation, outstanding spatial harmony within device sets, excellent reproducibility throughout numerous fabrication rounds, and also high manufacturing yield.
"The whole process can be automated as well as managed, making it intrinsically attractive for large and high-throughput manufacturing," the researchers stated.
The team thinks that the future of research study in this area must look in new ideal device interlayers to enhance the high quality of the active material and also the openness, passivating defects by vacuum-based techniques, as well as boosting operational security in order to optimize as well as realize the complete capacity of thermally evaporated perovskite solar devices.
Also read

