Ultra-thin silicon nanoparticle solar cell with 11% efficiency
- Iranian scientists have demonstrated a multi-layer silicon nanoparticle (SNP) solar cell based upon nanoparticles that are densely stacked inside a dielectric medium. They considered different SNP frameworks as well as arrangements to customize these particles as a p-- n junction cell.
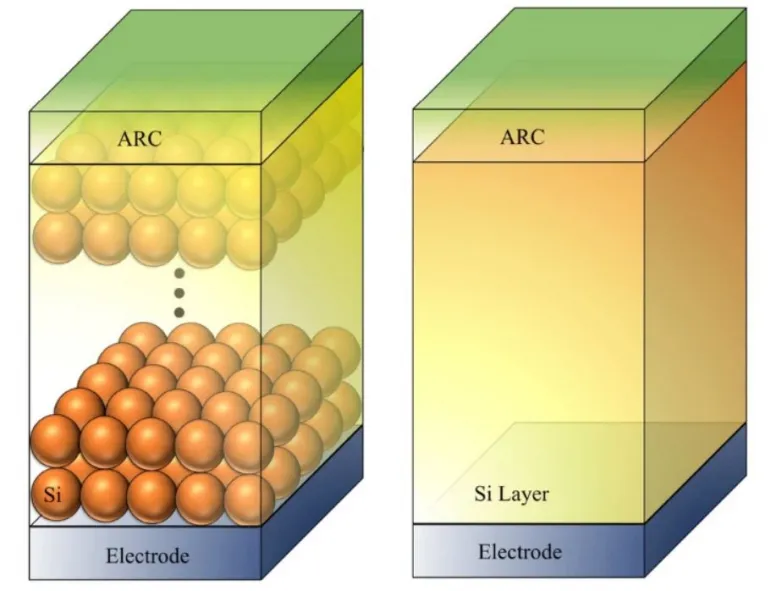
Researchers in Iran have actually suggested using multi-layer silicon dioxide (SiO2) nanoparticles as p-- n junctions in ultra-thin solar cells to enhance their photocurrent. The scientists demonstrated a multi-layer silicon nanoparticle (SNP) solar cell based upon nanoparticles that are densely stacked inside a dielectric medium.
" We demonstrate how this naturally textured architecture serves as a light absorber while having the possible to separate and also transport photo-generated providers," they stated. "We additionally assume a metallic call (silver) listed below, as well as an anti-reflection coating (ARC) over the absorbers to additional resemble a real cell."
They assumed that the nanoparticles were spherical with a selected distance of 300 nanometers and also a refractive index of 1.8, which is in line with values offered by products such as PEDOT: PSS as well as spiro-OMeTAD. They contrasted the absorption spectra of a multi-layer SNP absorber with two as well as 5 layers of silicon nanospheres to that of a flat layer and discovered that these particle-based structures give enhanced absorption, at longer wavelengths.
" Enhancing the variety of SNP layers decreases the advantage of the SNP framework in comparison to a planar one," they stated. "This shows that the SNP cell is optically better just when a few layers are made use of."
The research study group likewise found that a dense distribution of SNPs is better to sparse ones for solar cell applications.
" This is due to the fact that SNPs are thought to be the main absorber in the cell. Hence, any type of distance between them reduces the absorption of occurrence photons," the team stated.
They took into consideration various SNP structures and also setups to customize these particles as a p-- n junction cell. They said this type of cell can attain a theoretical effectiveness of around 11%.
" Furthermore, we revealed that by including silica nanoparticles of appropriate dimension in addition to the cell structure, one can enhance the photocurrent as much as around 10%," they stated.
They described the unique cell principle in "Layout and evaluation of multi-layer silicon nanoparticle solar cells," which was recently released in Scientific Reports.
" The cell configurations presented in this research provide improved optical absorption in an inherently textured structure," they said. "Interestingly, these attributes also occur for setups with random circulations of nanoparticles; this problem causes a streamlined way for fabrication of these ultra-thin cells."
An additional recent research at Penn State University reveals that nanoparticles enhance solar cell performance, however not for the factor the researchers expected.
" Yet this study shows that it does not matter if you put in up-conversion nanoparticles or any other nanoparticles-- they will certainly show the enhanced performance as a result of the enhance light spreading," they clarified.
They stated that by simply transforming the shape, dimension and also distribution of nanoparticles within the solar cells, higher performances could be attained.
" So some optimum form, circulation or size can actually bring about even more photocurrent delight," the Penn State group said. "That could be the future research instructions based upon concepts from this research study."
Also read

