Solar as well as wind create record 10% of international electricity
- Solar and also wind generated a record 9.8% of global electrical energy throughout the initial six months of 2020, but additional gains are needed if Paris Agreement targets are to be fulfilled, a new report has claimed.

Generation from both renewable energy resources rose 14% in H1 2020 compared to the very same period of 2019, while coal generation rolled 8.3%, according to the evaluation of 48 countries executed by climate brain trust Ember.
Given That the Paris Agreement was checked in 2015, solar and wind have more than increased their share of worldwide electrical power generation, rising from 4.6% to 9.8%, while several large countries have actually published similar change levels to both sustainable resources: China, Japan and Brazil all enhanced from 4% to 10%; the United States climbed from 6% to 12%; and also India's almost trebled from 3.4% to 9.7%.
The gains come as renewables catch market share from coal generation. According to Ember, the fall in coal generation was as a result of power need going down globally by 3% due to COVID-19, as well as due to climbing wind as well as solar. Although 70% of coal's autumn can be attributed to lower electrical power demand as a result of the pandemic, 30% is due to increased wind and also solar generation.
Indeed, an analysis released last month by EnAppSys discovered generation from Europe's solar PV fleet struck an all-time high in Q2 2020, driven by excellent weather conditions and a collapse in power need related to COVID-19. European solar produced around 47.6 TWh throughout the three months finished 30 June, assisting renewables take a 45% share of the complete electrical energy mix, equating to the largest share of any possession course.
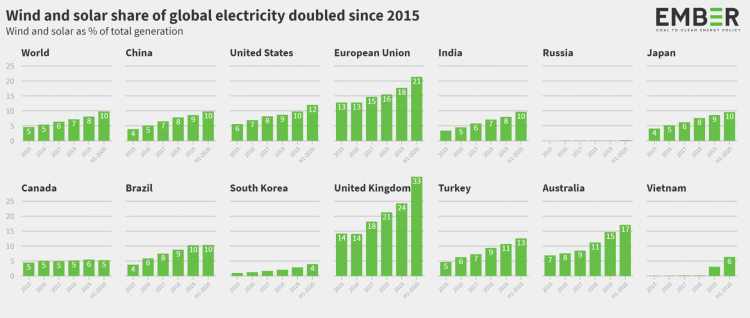
Inadequate progress
In spite of the quick trajectory from coal to wind as well as solar over the last five years, progress is until now inadequate to limit global temperature rises to 1.5 degrees, according to Ember. Dave Jones, senior electricity expert at Ember, stated the shift is functioning, but it's not taking place quickly enough.
" Countries across the globe are now on the same course-- structure wind generators and photovoltaic panels to replace electrical energy from coal as well as gas-fired power plants," he said. "But to keep a chance of limiting environment change to 1.5 degrees, coal generation needs to fall by 13% each year this years."
Also when faced with a worldwide pandemic, coal generation has only decreased 8% in the initial fifty percent of 2020. The IPCC's 1.5 level circumstances show coal needs to drop to just 6% of global generation by 2030, from 33% in H1 2020.
While COVID-19 has actually resulted in a drop in coal generation, interruptions triggered by the pandemic mean overall renewables implementation for this year will stand at around 167GW, down some 13% on implementation last year, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
In October 2019, the IEA suggested that as high as 106.4 GW of solar PV was to be deployed around the world this year. However, that price quote has actually dropped to around the 90GW mark, with hold-ups to building and construction and the supply chain, lockdown steps as well as emerging troubles in project financing stymying projects from finishing this year.
