Puncturing Sound to Enhance Solar Cell Effectiveness
- As culture relocations in the direction of a renewable energy future, it's vital that solar panels transform light into electrical energy as successfully as feasible. Some advanced solar cells are close to the academic optimum of performance-- and physicists from the University of Utah and also Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin have identified a method to make them also much better.
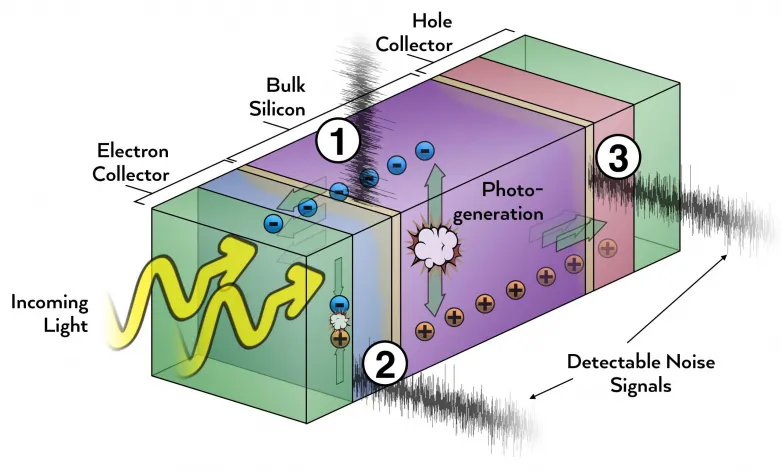
In a brand-new research, physicists made use of a strategy called cross-correlation sound spectroscopy to measure minuscule fluctuations in electrical present streaming between materials inside silicon solar cells. The scientists identified essential electrical noise signals that are completely unseen to traditional noise-measuring approaches. They were likewise able to identify the most likely physical procedures causing the noise, which often leads to a loss of energy as well as reduced performance.
" Determining noise on a things is fairly straightforward. You can simply buy gadgets that do it. However the trouble that pesters us is that these gadgets additionally have sound," stated Kevin Davenport, associate teacher of physics at the U as well as lead author of the paper. "This cross-correlation technique allows us to not only determine the noise of the tool, yet to also gauge the sound of our detector as well as remove it to ensure that we can see a lot, much smaller noise signals."
The strategy, which was released on June 24, 2021 in the journal Scientific Reports, is a vital brand-new tool to enhance product interfaces for a much better solar cell, or to examine ineffectiveness in other difficult tools.
" It's unexpected how vital little enhancements in performance are for market. Simply a portion of a percent renovation translates into billions of dollars as a result of the scale of manufacturing," said co-author Klaus Lips, professor of physics at Freie Universität Berlin as well as department head at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin where the solar cells have been designed as well as made.
" In the past, we have used the cross-correlation method to study rather simple research-grade light producing diodes, yet advantages of the method absolutely entered the light in this job," claimed Andrey Rogachev, teacher of physics at the U and also co-author of the research. "As well as it surpasses the solar sector. In any type of gadget with many layers, each user interface between products can reduce performance somehow. It's so complicated, you have to be truly very discreet to be able to claim what's going on as well as, much more significantly, where the particular sound is occurring. It turns out that this strategy permits us to do just that."
A single technique was not enough to comprehend complex devices. Interpretation of the noise information have actually been greatly aided by solar cell simulations performed by C.T. Trinh, a postdoctoral scientist at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and also co-author of the study. The last co-author is Mark Hayward, then an undergraduate study at the U as well as now a graduate student at College of California, Irvine.
Evaluating sound
The research study evaluated silicon heterojunction solar cells (HSCs), a premium kind of single-material solar cell as well as currently one of the most reliable of its kind on the market-- 26.7% of light that strikes the cell is converted into electrical power. On the other hand, the cells that make up photovoltaic panels on a household residence range in between 15% and also 20% effectiveness.
In an HSC, power generation starts when private bits of light called photons are taken in by the photo-active layer made from crystalline silicon and also develops sets of adversely billed electrons and favorably charged openings, which are charges brought on by missing out on electrons. Electrons and holes are then pulled in contrary instructions by an electric area created by 2 selective calls made of hydrogenated amorphous silicon modified with contaminations. This procedure generates existing that we use as electricity. The problem is that the selective electrode and photo-active silicon do not match with each other completely, developing problems that catch electrons. To get rid of these issues in research-grade solar cells like the ones in the research study, the researchers put in between them an ultrathin layer of pure amorphous silicon. Finally, all of these five layers are sandwiched between 2 layers of transparent conducting product, called ITO, as well as gold electrodes.
The effectiveness of HSCs depends on exactly how well the different layers are connected together. A mild mismatch in between 2 layers can make it challenging for the electrons to obtain where they need to go-- a problem that will produce a noise signal.
" That trouble is sort of surprise inside these interfaces, and it's actually hard to be able to find any kind of type of signal. However the noise strategy that we make use of is very conscious truly, actually tiny individual signals," stated Davenport. It's like paying attention to a note played by various tools, he continued. A C-note on a violin coincides as a C-note on a cello, yet they seem various. If you were to examine that note, you can take out information to find out something concerning the instrument that created it, like the size or product of the strings.
" We do something similar to that. We see this wide spectrum of various noise signals and also various settings along the frequency axis. We can say, 'OK, this part of the note that we see, we can attribute to this physical process and also this part is a various physical process,'" said Davenport. "However the gadget is full of these processes that all create noise as well as it's actually challenging to un-entangle them-- like pulling out a single voice in a 200-person carolers. This technique enables us to eliminate a great deal of the undesirable section of the signal."
Mapping inadequacies
The silicon HSCs are outstanding as they are, however they still have limitations. The study group's new method recognized essential areas in the gadget where certain physical procedures are generating electrical signals. In the future, little modifications at these stages can boost the effectiveness of these cells, as well as solar cells of the future. After sifting with the electrical cacophony to find the appropriate signals, the physicists ran a simulation to identify what physical procedures were happening at the area of the signal.
The future generation of solar cells are known as tandem cells, which are heaps of various photovoltaic or pv materials that are each conscious a various part of the sunlight's light, offering such a gadget a capacity to generate more power. One recommended device layer is the hot-ticket perovskite product.
"With each other, the new solar cell can appear the limit of the silicon tool on its own, beyond 30% effectiveness," stated Lips.
At this side of efficiency, tiny losses issue. One such loss has been observed by material scientists; the deposition of the clear ITO in some way modifies the underlying silicon layers, producing issues which lower the gadget's effectiveness. One of the major electrical noise signals that the scientists determined in this research went to this interface, where the fees are entraped and also released. An additional significant signal occurred as openings gone through a comparable obstacle on the rear end of the device.
"The capability to spot these signals indicates that we can comprehend their resources as well as alleviate them," claimed Davenport.
Also read

