New study directions in disordered carbon anodes for Na-ion batteries
- Na-ion batteries (NIBs) are gradually bring in much interest as a choice to lead-acid batteries as well as supplement to Li-ion batteries (LIBs) owing to the plentiful Na resources and excellent cost-effectiveness.
Considering that one of the most frequently made use of graphite as an anode product in LIBs can not be naturally utilized in NIBs, tremendous efforts have actually been made to advance the basic understanding as well as style of appropriate anode materials for NIBs, including the renovation of Na storage ability as well as the research on Na storage space devices. According to all these studies, disordered carbons are currently one of the most appealing anode prospects for NIBs. Nevertheless, there are still many obstacles require to be resolved, as well as the additional expedition of disordered carbon anodes is really important in the future.
Just Recently, Prof. Yong-Sheng Hu and also Prof. Yaxiang Lu from Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences systematically reviewed and suggested the future study directions of disordered carbon anodes for NIBs and also reviewed the current progression and also continuing to be difficulties.
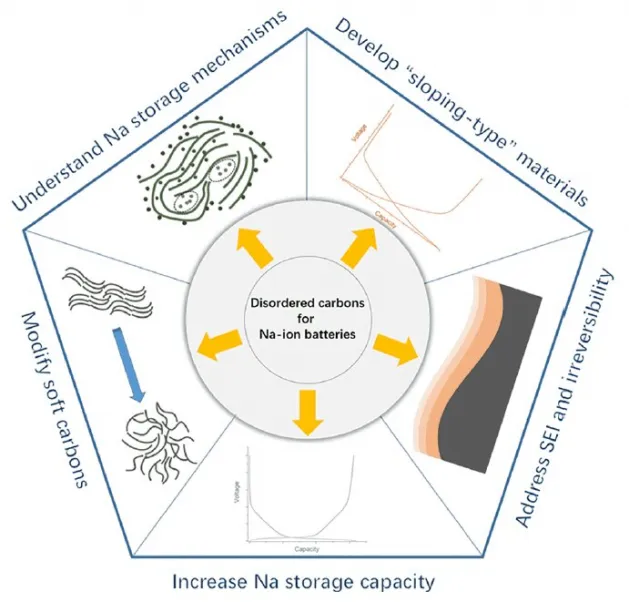
The writers initially summed up the landmarks of the studies on disordered carbons for Na storage space during the last decades, while there are still several difficulties as well as unresolved questions. The authors recommended 5 main study directions on disordered carbon anode products:
- Recognizing the existing conflicts and also portraying a complete picture of Na storage space devices in disordered carbons;
- Creating hard carbon anode products with ultrahigh Na storage space capacity over 400 mAh/g;
- Establishing "sloping-type" carbons in the direction of high-power and risk-free NIBs;
- Alteration of soft carbons for high cost efficiency;
- Understanding the strong electrolyte interphase and also enhancing the initial Coulombic performance.
The present study development for every instructions was summed up, as well as the continuing to be difficulties were reviewed. The writers additionally give possible services for each instructions. Early looks into have well laid the foundation of the research of disordered carbon anodes for NIBs and led the road from lab to commercialization. The authors think that additional research study is needed to address the remaining inquiries as well as damaging the bottlenecks of the disordered carbon anodes will put NIBs a great ahead.
Also read

