New room-temperature liquid-metal battery could be the course to powering the future
- Researchers in the Cockrell School of Engineering at The University of Texas at Austin have actually constructed a brand-new sort of battery that integrates the many advantages of existing choices while removing their crucial imperfections and also saving energy.
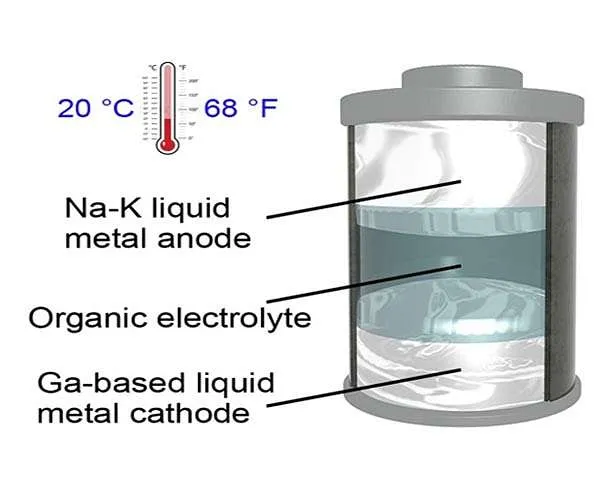
A lot of batteries are made up of either solid-state electrodes, such as lithium-ion batteries for portable electronics, or liquid-state electrodes, including circulation batteries for smart grids. The UT researchers have actually developed what they call a "room-temperature all-liquid-metal battery," that includes the best of both worlds of liquid- and solid-state batteries.
Solid-state batteries feature considerable capability for power storage space, but they usually experience various troubles that create them to break down over time and end up being less efficient. Liquid-state batteries can supply energy a lot more effectively, without the lasting degeneration of sold-state devices, but they either fail on high power needs or call for substantial resources to constantly heat up the electrodes and maintain them thaw.
The metallic electrodes in the group's battery can remain liquefied at a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius (68 degrees Fahrenheit), the most affordable operating temperature ever before recorded for a liquid-metal battery, according to the researchers. This represents a major change, due to the fact that existing liquid-metal batteries should be kept at temperature levels above 240 degrees Celsius.
" This battery can give all the benefits of both strong- as well as liquid-state - consisting of much more power, raised security and also adaptability - without the corresponding downsides, while also saving energy," stated Yu Ding, a postdoctoral scientist in associate professor Guihua Yu's research study group in the Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering. Ding is the lead writer of a paper on the room-temperature battery the team published lately in Advanced Materials.
The battery consists of a sodium-potassium alloy as the anode and also a gallium-based alloy as the cathode. In the paper, the scientists note that it may be possible to produce a battery with even lower melting points using different products.
The room-temperature battery guarantees more power than today's lithium-ion batteries, which are the foundation of a lot of personal electronic devices. It can charge and also supply energy a number of times much faster, the scientists claimed.
Due to the fluid parts, the battery can be scaled up or down quickly, depending on the power required. The bigger the battery, the more power it can supply. That versatility allows these batteries to possibly power every little thing from smartphones and also watches to the framework underpinning the motion toward renewable resource.
" We are thrilled to see that fluid metal could supply an appealing option to replace conventional electrodes," Professor Yu claimed. "Given the high power as well as power density demonstrated, this innovative cell could be possibly executed for both smart grid and also wearable electronic devices."
The researchers have spent greater than three years on this project, yet the work isn't done yet. Much of the elements that comprise the foundation of this brand-new battery are much more abundant than some of the key products in conventional batteries, making them possibly much easier and less expensive to produce widespread. Nonetheless, gallium remains a pricey material. Locating alternative products that can provide the very same efficiency while decreasing the price of manufacturing stays an essential challenge.
The next action to boosting the power of the room-temperature battery can be found in improving the electrolytes - the components that enable the electric charge to flow via the battery.
"Although our battery can not take on high-temperature, liquid-metal batteries at the current stage, much better power capacity is expected if progressed electrolytes are created with high conductivity," Ding stated.
Also read

