Multi-junction solar cell integrating radiative cooler
- The triple-junction solar cell is based upon indium gallium phosphide (InGaP), gallium arsenide (GaAs), as well as Germanium (Ge) and is made with a micro-grating made from glass, consisting of a two-dimensional x-framework structure repaired onto the surface of the solar cell. Its operating temperature level was found to be 6 degrees Celsius lower than that of a recommendation cell without the cooling technique.
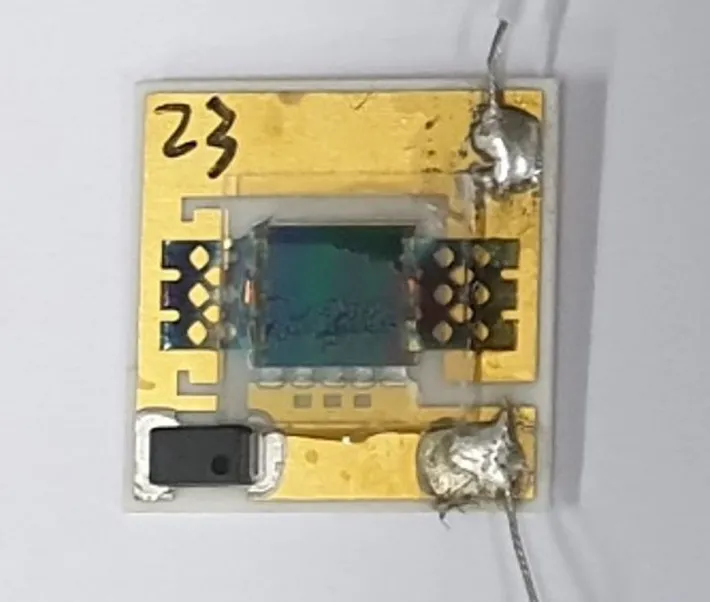
Researchers from the Pusan National University in South Korea have actually created a multi-junction solar cell that integrates a radiative cooler focused on lowering cell temperature level and raising power yield.
" Our radiative cooler technology might be applied to all type of solar cells but it is most appropriate for multi-junction solar cells with reduced bandgap, as it is the least prone to sub-bandgap heating" the research's equivalent writer, Gil Ju Lee.
Radiative cooling is the principle all objects on Earth often tend to emit part of the heat they receive from the sunlight's infrared radiation. The atmosphere presses that warm back to Earth, with the exception of infrared wavelengths, which can get away the ambience.
The triple-junction solar cell was based upon indium gallium phosphide (InGaP), gallium arsenide (GaAs), and also Germanium (Ge) and also was made with a micro-grating constructed from glass, containing a two-dimensional x-framework structure fixed onto the surface of the solar cell. This structure is asserted to be able to effectively produce the heat generated by the cell through the ambience right into deep space. "Our research study is the very first theoretical as well as speculative demo of the performance of radiative-cooler-integrated solar cells," the scientists stated.
A clear and clear ultraviolet curable adhesive was utilized to attach the cell with the cooler and also no anti-reflection covering was used on the cell. Gold metal was harmonized on the device's topside and plated on its bottom side, with sapphire being used as the substratum. "The solar power gain is considerably raised, particularly at the glazing angle, owing to the lengthened optical path produced by the diffraction of the light-trapping radiative cooling (LTRC)," the researchers discussed.
The efficiency of the solar cell with the radiative cooler was examined with outside field tests under approximately 900 Wm-2 direct sunshine and also was contrasted to that of a referral cell without the cooling strategy. The operating temperature level of the gadget with the cooler was discovered to be 6 degrees Celsius lower and its open-circuit voltage 2% greater. It likewise revealed a higher short-circuit current of 0.5 mA.
" Our radiative cooler is based on a very inexpensive glass product," Lee better explained, referring to the costs of the suggested technology. "An additional treatment must be included the glass material to make a micro-grating two-dimensionally on the surface of the glass and also, nevertheless, it could not be expensive due to the fact that the glass is cheap and also the technology for the micro-grating is mature."
He additionally mentioned the possibility of using the radiative cooler to change encapsulants in solar cells, which would certainly more than offset its additional costs, according to the researcher. "The radiative cooler may provide the same degree of protection," he highlighted, noting that the integration of the cooling technology in industrial solar module manufacturing may be accomplished conveniently, with larger scales assisting further lower the costs of the coolers.
The new technology was presented in the paper Determining the Effectiveness of Radiative Cooler-Integrated Solar Cells, published in Advanced Energy Materials. "The radiative cooling method provided in this research study is effective particularly for the multi-junction solar cells and likewise for focusing photovoltaic cells," the researchers concluded.
Radiative cooling was just recently applied to solar panel cooling by researchers from the Purdue University in the USA, the Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology and also the Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales in Spain, and also the Jordan University of Science and also Technology and also the Australian College of Kuwait.
A group of researchers from at the Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China has actually recently carried out a review of the possible combinations between radiative cooling (RC) methods and also solar energy systems of various kinds
Also read

