Harnessing solar energy: New method improves readings of double-sided panels
- A research laboratory in photonics and renewable energy at the University of Ottawa has actually developed a new method for determining the solar energy produced by bifacial photovoltaic panels, the double-sided solar modern technology which is expected to fulfill increased worldwide energy demands moving on.
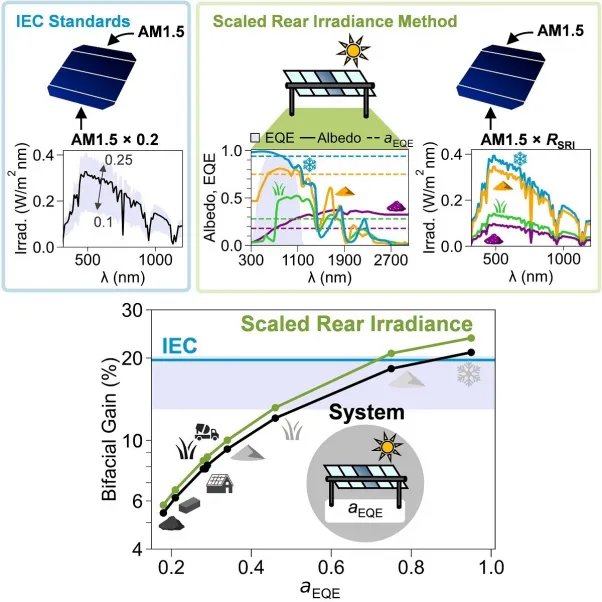
Released in the journal Joule, this research study from the SUNLAB group in the Faculties of Engineering and also Science recommends a characterization method that will certainly boost the measurement of bifacial panels indoors by thinking about external effects of ground cover such as snow, grass and also dirt. This will certainly offer a way to continually check bifacial photovoltaic panel efficiency indoors that properly represents exactly how the panels will execute outdoors.
With bifacial photovoltaics expected to supply over 16% of global energy demand by 2050, the SUNLAB's approach will certainly boost international device measurement standards which currently do not compare ground cover.
" Our recommended characterization method, the scaled rear irradiance method, is an improved method for indoor-measuring as well as modeling of bifacial devices that is representative of outdoor environmental conditions," claims Erin Tonita, lead author and a Physics Ph.D. pupil examining under Professor Karin Hinzer, whose research group creates new ways to harness the sun's energy.
" Incorporating this new method into future bifacial standards would certainly give a regular technique for testing bifacial panel efficiency under ground conditions including snow, grass, and also dirt, corresponding to internationally varying illumination conditions."
Photovoltaics is the research of transforming solar energy right into electrical energy through semiconducting products, such as silicon. In bifacial photovoltaic panels, the semiconducting product is wedged between two sheets of glass to enable sunlight collection on both sides, with one side usually angled towards the sun as well as the opposite angled towards the ground.
The extra light collected by bifacial solar panels on the rear-side offers a benefit over typical photovoltaic panels, with manufacturers touting approximately a 30% rise in production compared to traditional photovoltaic panels. Bifacial solar panels are additionally extra durable than standard panels as well as can create power for over thirty years.
" Implementation of this method into international standards for such panels can allow forecasts of outdoor bifacial panel efficiency to within 2% absolute," states Tonita, that expects the advantages of this methodology to include:
- Enabling comparisons between existing as well as arising bifacial innovations.
- Enhancing efficiency by means of ground cover specific layout optimization.
- Increasing photovoltaic panel deployments in non-traditional markets.
- Lowering financial investment risk in bifacial panel deployments.
- Improving bifacial panel manufacture datasheets.
"This method is of particular importance as renewable resource infiltration increases towards a net-zero world, with bifacial photovoltaics forecasted to contribute over 16% of the global energy supply by 2050, or around 30,000 TWh annually," claims Hinzer, creator of SUNLAB and the University Study Chair in Photonic Devices for Energy and a Professor at the School of Electrical Engineering as well as Computer Science.
"This will certainly expand existing International Electrochemical Commission standards for bifacial photovoltaic panel measurements, enabling exact comparisons of bifacial panel modern technologies, application-specific optimization, and also the standardization of bifacial panel power scores," adds Hinzer, whose SUNLAB researchers worked in cooperation with Arizona State University for the research study.
Also read

