Different combinations of PV-powered electrolysers
- An EU-funded study project worked with by German research study institute Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin has actually evaluated a number of configurations for solar-powered hydrogen generation. First results revealed which may be one of the most ideal PV modern technologies for electrolysis.
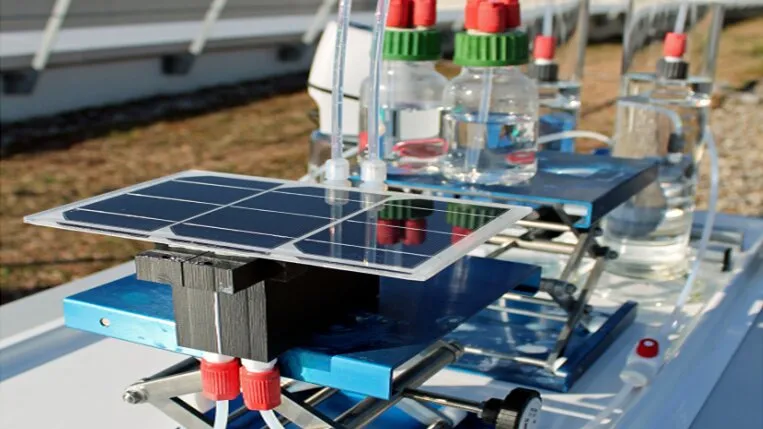
An EU-funded research project worked with by German study institute Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) has actually examined numerous configurations for solar-powered hydrogen generation in order to discover the very best combination in between the PV innovation and also electrolyzers.
The EUR2.5 million PECSYS project (Technology presentation of massive photo-electrochemical system for solar hydrogen manufacturing) was released in early 2017 with the goal of creating a prototype on a location of at the very least 10 square meters that transforms greater than 6% of the event solar energy into hydrogen while preserving stable operation for at the very least six months.
More than 3 years later on, the results of these initiatives have actually been released. "Initially the plan was to test different products and afterwards choose the very best for last implementation in a demonstrator. However, we quickly discovered that various strategies give different benefits. As opposed to deselecting numerous choices as well as maintaining only one, we therefore determined to explore a variety of innovations," said the project organizer, Sonya Calnan.
The study team worked, for instance, on a polymer electrolyte membrane layer PEM stack remedy developed by German institute Forschungszentrum Jülich that is said to get water input only on the cathode side. It checked the option's long-term outside procedure in sizes going beyond laboratory scale while staying clear of making use of platinum team metals. The used PV modern technologies were silicon-based heterojunction solar cells as well as copper, indium, gallium and (di) selenide (CIGS) gadgets, and also the former was liked as a result of its high performance, reduced temperature coefficient, high open circuit voltage and innate bifacial ability. "The action was justified by existing strategies to build several large manufacturing centers in Europe," the researchers stated, most likely describing plans by Swiss tech group Meyer Burger to establish a GW-sized heterojunction module manufacturing.
A pilot hydrogen facility was established with full-sized silicon heterojunction modules and also CIGS modules linked to polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolysers. "The installment created approximately 42.9 g/h of hydrogen with an ordinary solar to hydrogen performance of 10% over one month of constant exterior procedure," the research study group explained.
A 2nd experiment was conducted at the heterojunction solar module factory of Italian energy Enel, which is additionally a project companion, in Catania, southern Italy. "Bifaciality represents an innovative remedy to raise the hydrogen manufacturing yield without enhancing cost," Calnan claimed. "We might demonstrate a solar to hydrogen efficiency of 13.5 % as well as a hydrogen manufacturing price of 307 mg/h at a solar irradiation degree of 1,000 W/m2 and an ambient temperature of 25 ° C. This is an increase of 14 % compared to a monofacial procedure."
The project, funded by the Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation program, Hydrogen Europe as well as N.ERGHY, runs until completion of the year. The Competence Centre Thin Film and also Nanotechnology for Photovoltaics Berlin at the HZB led the sychronisation, bringing together expertise from the Jülich Research Centre (Germany), Uppsala University (Sweden), the National Research Council of Italy in addition to from 2 PV firms: Sweden's Solibro Research ABDOMINAL and also Italy's 3SUN.
Also read

