Basically endless solar cell experiments
- Osaka College researchers employed equipment finding out to make new polymers for usage in solar devices. After basically evaluating over 200,000 prospect materials, they manufactured one of one of the most encouraging and located its buildings were consistent with their predictions. This work may bring about a change in the way functional products are discovered.
Artificial intelligence is an effective device that enables computers to make forecasts concerning also complex scenarios, as long as the formulas are supplied with adequate example data. This is specifically beneficial for complicated problems in product scientific research, such as developing molecules for organic solar cells, which can depend on a huge array of variables and also unknown molecular frameworks. It would certainly take human beings years to sift through the data to locate the underlying patterns-- and also even longer to evaluate every one of the feasible prospect mixes of benefactor polymers and acceptor particles that compose an organic solar cell. Therefore, development in boosting the performance of solar cells to be competitive in the renewable resource area has been slow-moving.
Now, scientists at Osaka College utilized equipment learning to screen thousands of countless contributor: acceptor pairs based on a formula trained with information from previously published speculative research studies. Attempting all feasible combinations of 382 donor molecules as well as 526 acceptor particles resulted in 200,932 sets that were virtually examined by predicting their power conversion effectiveness.
"Basing the construction of our device leaning model on a speculative dataset substantially boosted the forecast accuracy," first author Kakaraparthi Kranthiraja claims.
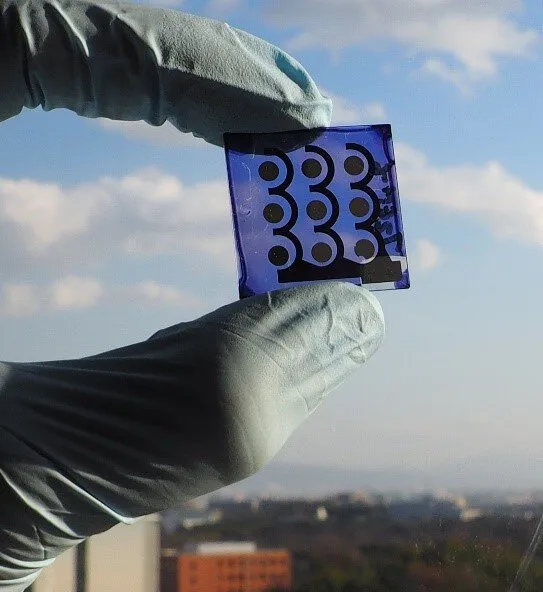
To validate this technique, among the polymers forecasted to have high performance was synthesized in the lab as well as examined. Its properties were discovered to adjust with forecasts, which offered the scientists much more confidence in their method.
"This project might contribute not only to the growth of highly reliable natural solar cells, yet also can be adjusted to material informatics of various other practical materials," senior author Akinori Saeki states.
We might see this kind of machine learning, in which a formula can quickly evaluate thousands or perhaps also countless prospect molecules based on artificial intelligence forecasts, applied to various other areas, such as stimulants and also useful polymers.
Also read

