Advancement of brand-new photovoltaic commercialization modern technology
- A modern technology to more increase the commercialization of Colloidal Quantum Dot( CQD) Photovoltaic( PV) gadgets, which are anticipated to be next-generation photovoltaic tools, has actually been established.
On the 30th (Monday), DGIST introduced that a study group of Professor Jongmin Choi from the Department of Energy Science as well as Engineering and also Professor Edward H. Sargent from the University of Toronto has actually recognized the reason for the efficiency destruction in CQD PV tools and also created a product handling approach with the ability of supporting the efficiency of the gadgets.
Quantum dots have outstanding light absorbance and also can taking in light over a wide variety of wavelengths. Therefore, they have actually obtained assumption as an essential product for the future generation photovoltaic gadgets.
Particularly, quantum dots are light, flexible, and also include reduced handling expenses; as a result, they can be changed by supplementing the downsides of silicon solar cells presently in operation
Hereof, a number of researches on photoelectric conversion effectiveness (PCE) have actually been performed with the objective of enhancing the efficiency of CQD PV tools. Nevertheless, really couple of researches have actually concentrated on boosting the security of these tools, which is required for the commercialization procedure. Particularly, couple of researches have actually made use of the CQD PV tool at the Maximum Power Point, which is the real operating atmosphere of PV tools.
For this function, the study group explored the sources of efficiency destruction by continually subjecting them to lighting and also oxygen for extended periods of time, comparable to the real operating problems, in order to boost the security needed for the real commercialization phase of CQD PV tools.
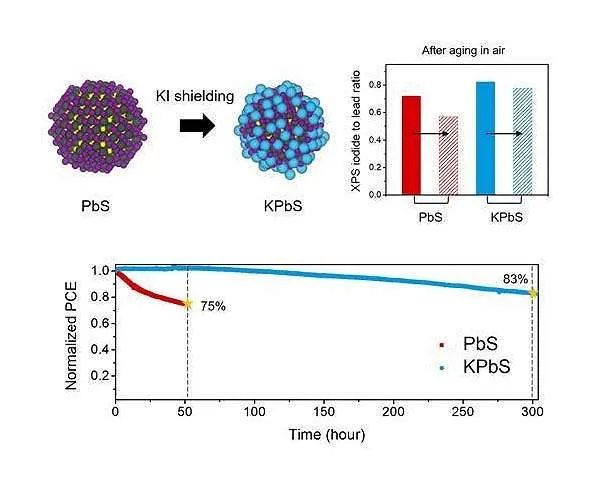
Therefore, it was determined that the iodine ions externally of the quantum dot solids were eliminated by means of oxidation, leading to the development of an oxide layer. This oxide layer caused the contortion of the quantum dot framework, consequently lowering the effectiveness of the tool.
The research study group established a ligand alternative approach with potassium( K) to enhance the reduced performance of the tool. Ligand describes the ions or particles that bond to the main atom of a facility comparable to a branch.
Below, potassium iodide, which avoids the oxidation of iodine, was released externally of quantum dot solids to undertake a replacement procedure. As a result of application of the developed approach, the gadget kept its continual efficiency price of over 80%, which is its preliminary effectiveness price, for 300 hrs. This number is a number that is greater than premeasured efficiency so far.
Teacher Jongmin Choi from DGIST claimed, "The research study is to show that the CQD PV gadget can run extra stably in the real operating atmosphere," and also even more commented, "The outcomes are anticipated to additional speed up the commercialization of the CQD PV tool. "
The outcomes of this research were released on February 20, in a world-leading, global scholastic journal Advanced Materials (IF = 25.809). Teacher Jongmin Choi from the Energy Science and also Engineering Department of DGIST took part in this research study as the lead writer.
Also read

