A much safer, more economical and rapid billing liquid battery
- Lithium-ion batteries are essential for modern life, from powering our laptop computers as well as cell phones to those brand-new holiday playthings. But there is a safety threat - the batteries can ignite.
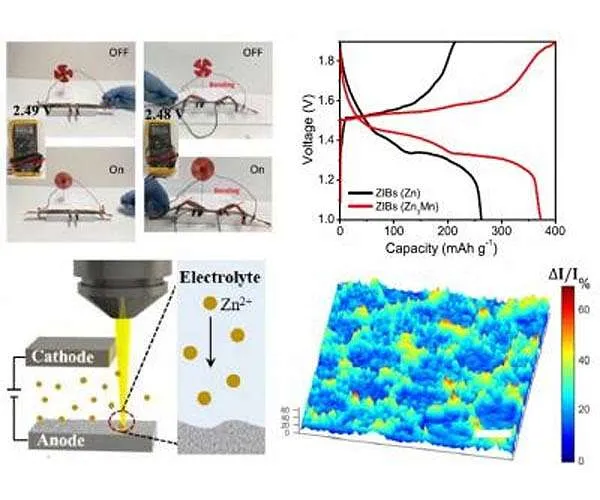
Zinc-based liquid batteries avoid the fire threat by utilizing a water-based electrolyte instead of the traditional chemical solvent. Nonetheless, unchecked dendrite development limits their capability to offer the high performance and also long life required for useful applications.
Now scientists have reported in Nature Communications that a new 3D zinc-manganese nano-alloy anode has actually gotten over the constraints, leading to a secure, high-performance, dendrite-free liquid battery utilizing salt water as the electrolyte.
Xiaonan Shan, co-corresponding author for the work and also an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Houston, stated the discovery uses promise for energy storage space as well as other applications, including electrical vehicles.
" It gives a low-cost, high power density, stable battery," he stated. "It should be of use for trustworthy, rechargeable batteries."
Shan as well as UH PhD trainee Guangxia Feng likewise established a sitting optical visualization strategy, allowing them to straight observe the response dynamics on the anode in real time. "This platform provides us with the ability to straight picture the electrode reaction dynamics sitting," Shan claimed. "This important info gives direct proof and also visualization of the reaction kinetics as well as aids us to recognize sensations that could not be easily accessed previously."
Checking determined that the unique 3D zinc-manganese nano alloy anode remained stable without degrading throughout 1,000 hours of charge/discharge cycling under high present density (80 mA/cm2).
The anode is the electrode which releases current from a battery, while electrolytes are the tool whereby the ionic fee moves in between the cathode and also anode. Using salt water as the electrolyte as opposed to highly detoxified water offers an additional method for reducing battery cost.
Standard anode materials utilized in aqueous batteries have been prone to dendrites, little developments that can create the battery to lose power. Shan and also his associates recommended and showed an approach to effectively reduce as well as subdue dendrite formation in aqueous systems by managing surface area response thermodynamics with a zinc alloy and also reaction kinetics by a three-dimensional framework.
Shan stated scientists at UH as well as University of Central Florida are currently investigating other metal alloys, in addition to the zinc-manganese alloy.
Also read

